drop arm rotator cuff injury test|positive drop arm test : manufacturer Purpose [edit | edit source]. To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test.. Evidence [edit | edit source]. Based on the Park et . WEB26 de abr. de 2023 · Para fazer o primeiro acesso no aplicativo utilizando e-mail e .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Lançado em janeiro de 2014, o gshow se estabeleceu no mercado digital como o grande portal de entretenimento nacional. 'Jornal Nacional' anuncia lançamento do gshow. "O ‘Big Brother’ é um programa que muda a curva da internet no Brasil." "O consumidor de entretenimento está na rede social."
shoulder test for rotator cuff
A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers. Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.
Rotator cuff tear (Supraspinatus) Drop Arm Test / Codman's Test; Empty Can Test; Full Can Test; Rotator cuff tear (Supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles) and shoulder impingement External Rotation Lag Sign; Rotator cuff tear .
general tools pinless moisture meter for concrete
Purpose [edit | edit source]. To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test.. Evidence [edit | edit source]. Based on the Park et .This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is . Rotator cuff injuries represent a common cause of shoulder pain. The rotator cuff tendons, particularly the supraspinatus tendon, are uniquely susceptible to the compressive forces of subacromial impingement. . Painful arc test, drop arm test, and weakness in the external rotation is the most common observations on physical examination.The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:
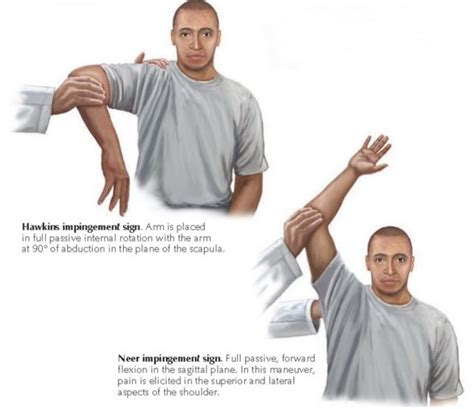
The aim was to assess diagnostic accuracy of 15 shoulder special tests for rotator cuff tears. From 02/2011 to 12/2012, 208 participants with shoulder pain were recruited in a cohort study. Among tests for supraspinatus tears, Jobe’s test had a .Jobe’s test; Drop arm test; Neer test; Test for Teres minor: Hornblower’s Sign; To enhance the ability to detect full-thickness rotator cuff tears, a test-item cluster has been developed. A cluster improves the post-test probability for the clinical diagnosis of a full-thickness tear.
Drop Arm Test. This simple test assesses the possibility of a rotator cuff tear. During the test, the patient (either sitting or standing) holds their arm straight out at a 90 degree angle, then slowly lowers the arm down to their side. The provider is looking for the patient’s ability to raise and lower the arm in a controlled manner. A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11).
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Empty Can Test, also known as the Jobe or Supraspinatus test, is used to assess for lesions of the rotator cuff, specifically the supraspinatus muscle and supraspinatus tendon.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patients arm is actively abducted to 90 o; The examiner applies downward resistance to the abducted arm; With the patient's hand in . Drop arm test. Pain with Jobe test. Infraspinatus. ER weakness at 0° abduction. ER lag sign. Teres minor. ER weakness at 90° abduction and 90° ER. Hornblowers. . select patients with a low-grade partial articular sided rotator cuff tear . rotator cuff repair (arthroscopic or mini-open) indications. acute full-thickness tears. The drop arm test is used to assess for rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. Interpretation. Drop arm test is negative if the patient is able to control the lowering of the arm slowly and without pain. Drop arm test is positive if there is pain while lowering the arm, .As the name suggests, if the arm drops suddenly, there is a likelihood of a rotator cuff tear. The inability to hold the arms at 90 degrees because of pain or weakness is seen as a positive result of for the test. The Drop Arm Test can be more accurate when used along with a combination of other tests like the Empty/full can test, External .
The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tears. How to Perform Drop Arm Test. Position of Patient: Patient is sitting or standing with arm relaxed at side. Performance: .The Drop Arm Test is a simple yet effective way to assess the integrity of your rotator cuff, particularly the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons, which are connected to the upper arm bone.
Codman's test is typically used in the assessment of a suspected rotator cuff tear. This test is also commonly referred to as the drop-arm test or sign. Technique [edit | edit source] The therapist passively raises the patient's arm to 90 degrees of abduction. The patient then lowers the arm back to neutral with the palm down.
Drop arm test: The patient’s shoulder is brought into a position of 90 degrees of shoulder abduction in the scapular plane. The examiner initially supports the limb and then instructs the patient to adduct the arm to the side of the body slowly. . Rotator cuff injuries represent a common cause of shoulder pain. The rotator cuff tendons .
When it gets torn, it can cause shoulder pain and weakness. Drop Arm Test – Positive vs. Negative. At this point, you might be wondering, how do I know if I have a rotator cuff tear? The answer is the “drop arm sign” test. This is a simple test you can do at home to see if you have a rotator cuff tear. To do the drop arm sign test:Purpose [edit | edit source]. This is a shoulder special test which is meant to assess the integrity, and tears, of the supraspinatus (SSP) and infraspinatus muscles (muscles which collectively contribute to the rotator cuff complex). This test can also be used for the clinical examination of a shoulder impingement syndrome (SIS).. Another name for this test is the Infraspinatus . Background It is unknown which combination of patient information and clinical tests might be optimal for the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears. This study aimed to determine the diagnostic value of nine individual clinical tests for evaluating rotator cuff tear and to develop a prediction model for diagnosing rotator cuff tear. Methods This prospective cohort study . Drop Arm Test . Your healthcare provider may perform the drop arm test if they think you may have a rotator cuff tear in your shoulder. For this test, the provider will lift your arm out to the side of your body while keeping it straight. They then drop your arm (hence the name of the test).
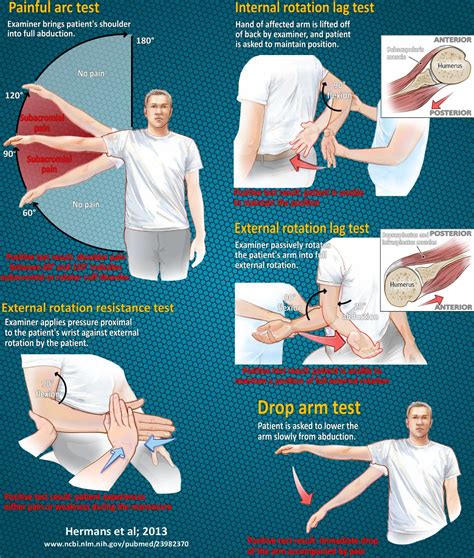
Rotator cuff injury test types. Which tests are performed may depend, in part, on whether your suspected rotator cuff injury is in the supraspinatus, . If you feel pain or weakness is detected, this indicates a supraspinatus tear. Drop arm test: This is to test for a full-thickness rotator cuff tear of the supraspinatus or, less often, the . Mindre gennemgående rotator cuff-skader udvikler sig gradvist, og læsionen bliver større hos 40% af patienterne efter 10 år3 ; Rotator cuff-skader kan udvikle sig til rotator cuff-artropati, hvor patienterne udvikler svære artrit/artrose forandringer i glenohumeralleddet samt pseudoparalyse af armen på grund af globale rotator cuff-skade A positive drop arm test indicates a potential rotator cuff tear or injury. If the patient is unable to maintain control of their arm during the descent, experiences pain, or has weakness in the affected shoulder, it suggests a significant rotator cuff problem. Further diagnostic imaging, such as an MRI, may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
A supraspinatus tear is a tear or rupture of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle. The supraspinatus is part of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Most of the time, it is accompanied by another rotator cuff muscle tear.This can occur due to trauma or repeated micro-trauma and present as a partial or full-thickness tear. Quite often, the tear occurs in the tendon or as an .It is used to test for the strength of the teres minor. Weakness or pain can indicate a tear. Technique [edit | edit source] The patient is in a standing position. The patient's arm is passively elevated to 90 degrees in the scapular plane, by the examiner . If a large posterior rotator cuff tear is present, the patient would not be able ot .
general tools pinless moisture meter review
De maneira dinâmica, mantendo todos os dados pessoais d.
drop arm rotator cuff injury test|positive drop arm test